Cyber Risk has consistently featured amongst the top three risks for Boards ever since the world started witnessing a spike in frequency of data breach incidents coupled with the introduction of some of the most stringent data privacy regulations across various jurisdictions. In particular, the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in early 2018 was recognised as a watershed moment which heightened the concern of Boards about financial and reputational implications of breach incidents.
Fast forward to 2021, the world is grappling with increased cyber-attacks as a result of remote working arrangements necessitated by the pandemic. The blurring boundaries between personal and professional spaces, mobile devices connecting to official networks, less secure home networks, inter-connectivity and reliance of IT on external technological service providers for scalability and cost efficiency has exponentially increased the cyber-attack surface for organisations and economies.
As per Willis Towers Watson’s Global Cyber Claims data from 2007 to 2020, the average cyber event cost was USD 2.8 Million with the largest cyber loss reported being USD 310 Million. IBM’s ‘Cost of Data Breach Report 2020’ notes the average cost of a data breach in India is INR 14 Crores.
The below chart shows the top loss events globally, by frequency and average size of the loss. The size of the bubble represents the total cost of each event category.
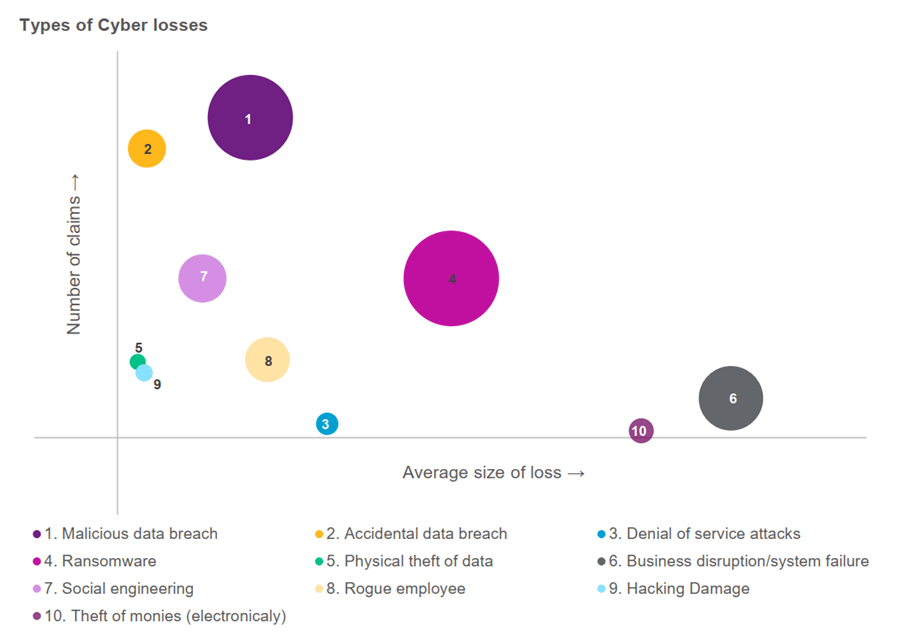
Source: Willis Towers Watson’s Global Cyber Claims Experience 2021
While Ransomware has been a looming risk since the early part of the decade, the world is witnessing its true devastating impact on organisations, communities and economies. The ‘Wannacry’ ransomware attacks of 2017 shortly followed by the ‘Notpetya’ ransomware attacks demonstrated the systemic downstream risks of cyber events, and exploits continue to peak in 2020 and 2021. As evident in the above chart, Ransomware risk is anticipated to be the costliest loss event category in 2021. According to Willis Towers Watson's claims data, the global average ransomware event cost is USD1.53 Million. Average ransomware demand observed in 2020 was between USD 4 - 4.5 Million (up from under USD 3.5 Million in 2017), with the average ransom payment noted as slightly above USD 1.6 Million. According to Sophos’ ‘State of Ransomware 2021’ report, India is statistically the most impacted, with average ransomware remediation costs of USD 1.1 Million and average ransom payment being USD 76,619.
Ransomware has also recently emerged as a preferred vector for state sponsored activism and espionage with entities in the critical infrastructure sector of rival nations being the prime targets. The ransomware attack on Colonial Pipeline in May 2021 where the entity reportedly paid a ransom of USD 4.4 Million (though some of this has been recovered by US investigators) demonstrates to nations and organisations the threat of ransomware as real and imminent.
The below chart maps the incidence of ransomware claims reported to Willis Towers Watson over the past couple of years:
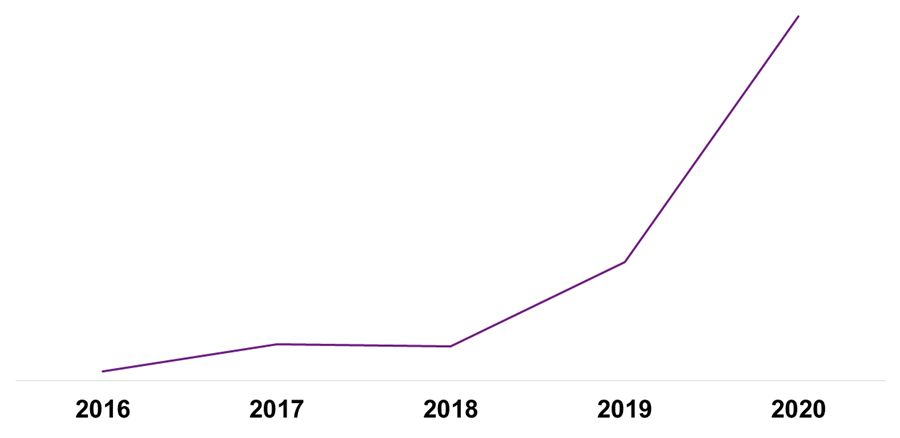
Source: Willis Towers Watson Global Cyber Claims Report 2020
Heightened reliance on Managed Service Providers (MSPs) and Cloud based technology over the years has resulted in supply chain risk in the form of downstream impact on reliant companies. Threat Actors are exploiting unpatched and zero-day vulnerabilities in the technologies and infrastructure of service providers with an intention to exfiltrate data or hold victim organisations to ransom over the exfiltrated data. The hack of Microsoft exchange servers earlier this year, IT management software of Solarwinds, and recent ransomware attack on the VSA software of Kaseya exemplify the significant downstream impact on thousands of companies across the globe.
Although, Ransomware and Supply Chain risks have dominated the cyber loss trends in 2021, the Business Interruption Losses resulting from the above-mentioned exploits have the next highest average severity of losses as per the Willis Towers Watson's Claims report.
Social Engineering Frauds particularly ‘Business Email Compromise’ (BEC) attacks have been the most frequent cyber loss category for organisations across the globe, especially in India. Owing to the relatively poor cyber awareness amongst employees, Indian enterprises across sectors have been one of the most widely affected in the world due to BEC attacks. While impersonation of vendors and suppliers causing invoicing frauds has been the most frequent loss in this category, the impersonation of senior executives has been found to be the costliest Social Engineering fraud category as per the insurance claims experiences.
Multiple reports and sources highlight that the Cyber Insurance claims experience in Asia has been tough (with certain cyber insurers experiencing a 120%+ loss ratio). Insurers in Asia overall have observed a 485% increase in the ransomware related claims. The steep rise in loss ratios in the cyber insurance space in Asia has resulted in rise in Cyber Insurance premium rates ranging from 40 -200% (the global average being north of 50%) depending on the nature of risk and the cyber security maturity levels of the Insureds. A key takeaway of Claims data suggest that cyber insurers are paying out on claims and policies are in action. While cyber claims in India, even couple of years ago were relatively infrequent, the volume of notifications and number of significant claims experienced in India show that cyber insurance is increasingly proving to be a valuable investment and critical part of an organisation’s overall risk management and financial recovery strategy.
Despite the most mature cyber security infrastructure, no security can be 100% in the current risk landscape. With the sophistication of cyber threat actors rising arguably at a swifter rate than cyber defense technologies, it would be wise for organisations to have pro-active risk management considerations around cyber risk management. Risk managers must invest in ‘Risk Identification’ and ‘Risk Analysis’ by employing cyber loss quantification and modeling exercises through collaboration with risk consultants followed by employing optimum risk transfer mechanisms in the form of appropriately structured Cyber and Crime Insurance programmes.
This article was first published in BWDisrupt.
| Title | File Type | File Size |
|---|---|---|
| Ransomware – Cyber Loss Trends 2021 | .2 MB |